Properties & Applications of Nano Zirconium Carbide
Zirconium carbide is a hard, high melting point material, and an excellent high-temperature refractory material. Nano zirconium carbide is a kind of common zirconium carbide. Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties, nano zirconium carbide enjoys a wide application in industrial production. In this article, let's take a deeper look at the properties & applications of nano zirconium carbide.

Properties & Applications of Nano Zirconium Carbide
Properties of Nano Zirconium Carbide
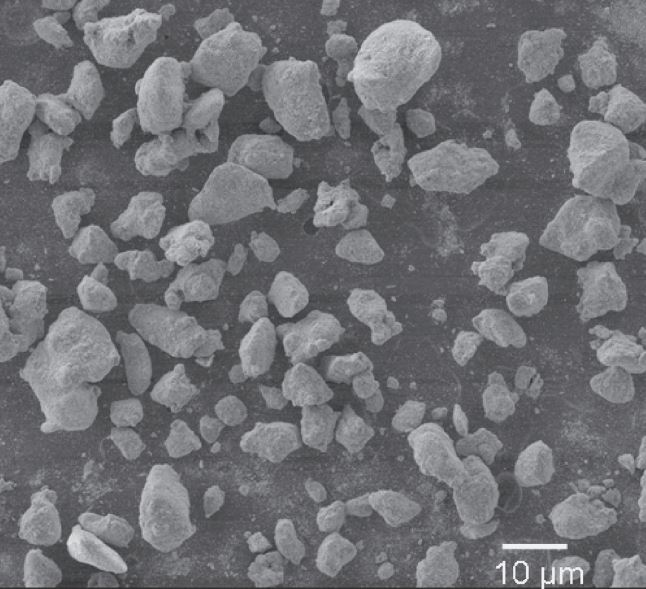
- Nano-zirconium carbide has the characteristics of high purity, small particle size, uniform distribution, large specific surface area, high surface activity, and low loose density.
- In addition, it also has excellent characteristics of high-temperature resistance, oxidation resistance, high strength, high hardness, good thermal conductivity, and good toughness.
- Nano zirconium carbide is also an important high-temperature structural material with a high melting point, high strength, and corrosion resistance, and has the characteristics of efficiently absorbing visible light, reflecting ultraviolet light, and energy storage.
Applications of Nano Zirconium Carbide
- Application of Nano Zirconium Carbide in New Thermal Insulation and Temperature Regulating Textile
Nano-zirconium carbide has the characteristics of efficiently absorbing visible light and reflecting infrared rays. It can absorb short wavelengths below 2μm and reflect infrared wavelengths exceeding 2μm. Through energy conversion, it prevents human body heat loss.
- Nano Zirconium Carbide Can Be Applied to Fiber
When the ZrC content in the fiber reaches two ten thousandths (by weight), the fiber has the best near-infrared absorption performance. The near-infrared absorption effect of adding ZrC to the fiber shell layer is better than that of adding ZrC to the core layer.
- Application of Nano Zirconium Carbide in High-Temperature Coating
The melting point of nano-ZrC is 3540℃. ZrC ceramics have good mechanical properties and high-temperature resistance under high-temperature and harsh environments. It is one of the essential materials in the aerospace field.
- Application of Nano Zirconium Carbide in Cemented Carbide
ZrC is an important high-temperature structural material with a high melting point, high strength, and corrosion resistance. The strength and corrosion resistance of cemented carbide with nano ZrC is greatly improved.
- Application of Nano Zirconium Carbide in Metal Coating Materials
The low-density loose ZrC coating has good thermal stress resistance and insulation properties and can be used as an insulating material; the high-density dense ZrC coating has good penetration resistance and can be used as a protective coating.
- Application of Nano Zirconium Carbide in Nuclear Industry
Nano ZrC has high-high temperature strength, high hardness, small thermal neutron absorption cross-section, and good radiation resistance. It is used as a new material for coating nuclear fuel particle barriers.
- Nano Zirconium Carbide Used as Abrasives
Nano ZrC has a Mohs hardness of 8-9 and good thermal conductivity. It is a good substitute for abrasives.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading our article and we hope it can help you to have a better understanding of the properties & applications of nano zirconium carbide. If you want to learn more about nano zirconium carbide, we would like to advise you to visit Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) for more information.
As a leading supplier of zirconium carbide products across the world, SAM enjoys over two decades of experience in the manufacture and sale of zirconium carbide powder and nano zirconium carbide powder. As such, we are confident that SAM will be your favorite zirconium carbide supplier and business partner.