How to Analyze the HA Content in the Fermentation Broth?
Introduction
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring polysaccharide that is widely used in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and biomedical industries. The production of HA typically involves the fermentation of bacterial strains, and the analysis of HA content in the fermentation broth is a crucial step in the production process to ensure the quality and purity of the final product. In this article, we will discuss the methods to analyze the HA content in the fermentation broth. Hope that you can learn about their advantages and disadvantages and select suitable HA products for your research or business.
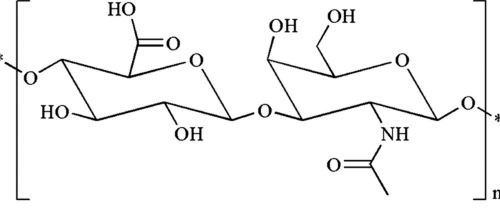
[1]
Figure 1. Chemical Structure of HA
How to Produce HA Using the Fermentation Broth?
Hyaluronic acid was extracted from rooster combs conventionally, yet this approach was abandoned for its low extraction rate, complex isolation process, and huge cost. Nowadays, a large scale of HA is produced via microbial fermentation, where HA is prepared by hyaluronan synthase enzymes in living microorganisms. It has the following benefits.
- New Nutrients: Some new substances that are beneficial for absorption are created.
- Higher Extraction Rate: Proteases, cellulases, and other enzymes promote plant cell rupture and the release of active ingredients in the process, thus increasing the yield and the extraction rate of HA consequently.
- Easier to Absorb: Polypeptides, polysaccharides, and other nano-sized small molecules are generated, which are easier to be absorbed.
- Fewer Side Effects: Microbial cells are able to decompose harmful substances and reduce unsafe factors.
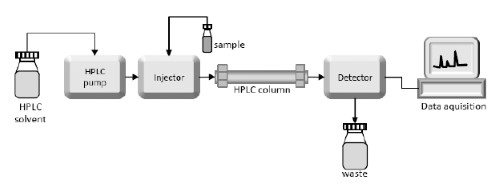
[2]
Figure 2. Diagram of HPLC Systems
Related reading: Does Fermented Skincare Work?
How to Analyze the HA Content in the Fermentation Broth?
Numerous techniques have been employed in order to improve the efficiency, productivity, and purity of hyaluronic acid production. Among them, several approaches are used for the analysis of the HA content in the fermentation process.
- Precipitation with Cetylpyridinium Chloride
Precipitation with cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) is a traditional analytical method, and it is followed by spectrophotometric measurement at 540 nm. However, it has limitations, such as interference from other polysaccharides and low accuracy.
To overcome these limitations of CPC, various analytical ways have been developed in recent years. One such method is high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). HPLC involves the separation of HA molecules based on their molecular weight, followed by detection using a UV detector. HPLC has been extensively employed due to its high sensitivity, accuracy, and selectivity. You can employ HPLC to analyze both the molecular weight and content of HA in the fermentation broth.
Another method that has gained attention recently is capillary electrophoresis (CE). CE is a high-resolution analytical technique that separates HA molecules based on their charge-to-size ratio. It can analyze both the molecular weight and content of HA in the fermentation broth with high resolution, low sample consumption, and short analysis time.
- Infrared Spectroscopy
In recent years, efforts have been made to develop new analytical methods that can overcome the limitations of existing methods. For example, a new method based on infrared spectroscopy (IR) has been evolved. The method involves the direct measurement of the absorption spectra of HA molecules, and the results are compared to a calibration curve to determine the HA content. This means has advantages such as high sensitivity, low cost, and simple sample preparation.
- Other Methods
In addition, other methods have been generated. For example, you can use mass spectrometry (MS) to analyze the molecular weight and content of HA by detecting the ions produced by the HA molecules. Gel permeation chromatography (GPC) can also be applied to separate HA molecules based on their molecular weight, which is followed by spectrophotometric measurement at 205 nm.
Table 1 shows the good points and weak points of these methods. You can check it for more information.
Table 1. Comparison of Different Analysis Methods of HA Contents
|
|
Process |
Detection |
Advantages/ |
Disadvantages |
|
Precipitation with Cetylpyridinium Chloride |
Precipitation with cetylpyridinium chloride;
|
By spectrophotometric measurement at 540 nm; |
Easy to carry out; Require fewer reagents and equipment; |
Interfere from other polysaccharides; Low accuracy; |
|
High-performance Liquid Chromatography |
Separation of HA molecules based on their molecular weight;
|
Using a UV detector; |
High sensitivity, accuracy, and selectivity; |
Require expensive equipment and trained personnel; Time-consuming; |
|
Capillary Electrophoresis |
Separation of HA molecules based on their charge-to-size ratio; |
Using a UV detector and optics. |
High resolution; Low sample consumption; Short analysis time; |
Requires specialized equipment and expertise; Sensitive to electrode contamination; |
|
Infrared Spectroscopy |
Direct measurement of the absorption spectra of HA molecules; |
Using an IR spectrometer. |
High sensitivity; Low cost; Simple sample preparation; |
Less accurate; Some impurities or contaminants can interfere with the measurement. |
Conclusion
In a word, the analysis of HA content in the fermentation broth is of great importance for the production of HA. Various analytical methods have been developed, each with its limitations and advantages. The choice of method depends on factors such as the sample matrix, the sensitivity and accuracy required, and the equipment and resources available. The development of new analytical methods is essential to improve the accuracy, sensitivity, and cost-effectiveness of the analysis of HA content in the fermentation broth.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a reliable supplier of quality hyaluronic acid of different grades and molecular weights. Send us an inquiry if you are interested.
Reference:
[1] Wang, Yan & Cai, Li-Quan & Nugraha, Bramasta & Gao, Yi & Leo, Hwa. (2013). Current Hydrogel Solutions for Repairing and Regeneration of Complex Tissues. Current medicinal chemistry. 21. 10.2174/0929867321666131212151855.
[2] Czaplicki, Sylwester. (2013). Chromatography in Bioactivity Analysis of Compounds. 10.5772/55620.








