Indium Applications Across Industries: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Indium, a remarkable metal renowned for its exceptional properties, is a cornerstone in various industries. This article delves into the diverse applications of indium, shedding light on its pivotal role in electronics, semiconductors, solders and alloys, atomic energy, and even promising areas like stomatology.
Overview of Indium Applications
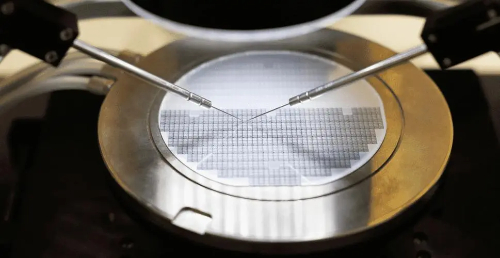
ITO Target
A significant proportion of global indium consumption, approximately 70%, is attributed to the production of Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) targets. These targets, consisting of high-purity indium oxide and tin oxide, play a crucial role in manufacturing transparent conductive electrodes for plasma and LCD TV screens, as well as sensitive elements for gas measurement.
Electronics, Semiconductors, and Radio
In the realm of electronic, semiconductor, and radio industries, indium's high boiling point, low resistance, and corrosion resistance make it indispensable. This section explores the extensive applications of indium in semiconductor materials and its contribution to creating special contact devices through a mixture of indium and silver oxides.

Solders and Alloys
Termed as the "indium alloy vitamin," the addition of indium enhances the strength, ductility, wear resistance, and anti-corrosion properties of many alloys. This section delves into the versatility of indium alloys, finding applications in solar cells, electric vacuum instruments, and beyond.

Atomic Energy Industry
Indium takes center stage in the atomic energy industry, serving as an indicator for neutron detection and contributing to the manufacture of control rods in nuclear reactors. This section highlights the efficacy of indium in creating neutron detectors with performance comparable to gallium.
Bearings and Coatings
Indium's impact on industrial bearings is explored in this section, where its application significantly extends service life. Additionally, the use of indium and gallium alloys in lubricating sliding elements is discussed, especially in electric vacuum instruments.
Fusible Alloys
The low melting point of indium is harnessed in this section, focusing on the production of fusible alloys used in diverse applications such as fuses and thermostats.
Stomatology
The burgeoning applications of indium in stomatology take center stage, with a focus on its role in creating dental inlay materials and enhancing corrosion resistance and hardness in filled materials.
Other Indium Product Applications
This section delves into specific indium compounds and their applications, including the manufacture of colored glasses and the use of indium halides in metal halide lamps, thereby improving lighting output and spectrum quality.
Indium compounds, such as oxides, sulfides, and phosphates, play a crucial role in the manufacture of colored glasses. These compounds impart distinctive hues to the glasses, contributing to a wide array of applications, from artistic glassware to specialized optical lenses.
Furthermore, indium's significance extends to the realm of metal halide lamps. Indium halides, particularly indium iodide, serve as valuable additives in these lamps. The inclusion of indium halides is designed to achieve two key objectives: improving lighting output and enhancing spectrum quality. The result is a more efficient and high-quality illumination, making indium a sought-after component in the lighting industry.
As technology continues to advance, the utilization of indium compounds in glass manufacturing and lighting applications underscores its adaptability and importance in enhancing both aesthetics and functionality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, indium's versatility shines across a spectrum of industries, as outlined in this comprehensive overview. Stanford Advanced Materials, at the forefront of material innovation, recognizes the pivotal role of indium in advancing technology and industrial applications.
By understanding the manifold applications of indium, we gain insight into its critical role in shaping the future of various industries, thanks to its unique properties and the ongoing research and development efforts facilitated by Stanford Advanced Materials.