Chlorine Trifluoride for In Situ Cleaning of CVD Chambers in Semiconductor Manufacturing: Cons and Pros
Introduction
One popular cleaning gas used in the semiconductor industry for in situ cleaning of CVD chambers is Chlorine Trifluoride (ClF3). ClF3 has many advantages and challenges because of its highly reactive and corrosive nature. In this article, we will explore these advantages and disadvantages, as well as safety considerations for its use in semiconductor cleaning applications. This information will help you learn how to use this gas safely and efficiently for the in situ cleaning of CVD chambers.
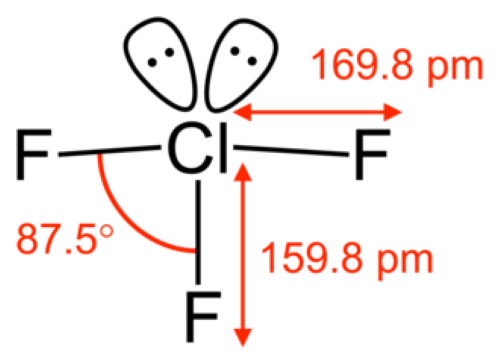 [1]
[1]
Figure 1. Chlorine Trifluoride
Understanding In Situ Cleaning and Its Importance in Maintaining CVD Efficiency
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a critical process for the semiconductor industry that allows for the precise deposition of thin films of materials onto substrates. Over time, the CVD chamber can become contaminated with by-products of the deposition process, such as carbon and metal residues. These contaminants, if left unaddressed, can have detrimental effects on the quality and reliability of semiconductor materials and devices. Therefore, in situ cleaning of CVD chambers is essential for maintaining the performance and functionality of CVD chambers.
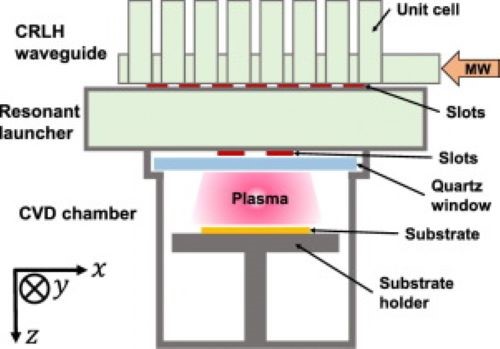 [2]
[2]
Figure 2. CVD Chamber
A typical in situ cleaning process involves the following aspects:
1. Residue Removal: The primary goal is to eliminate residues that accumulate on the inner surfaces of CVD chambers during semiconductor fabrication processes. These residues may include by-products of the deposition process, native oxides, metal fluorides, and organic contaminants.
2. Maintenance of Chamber Performance: The cleaning helps maintain the performance and functionality of the CVD chamber, ensuring consistent and reliable deposition processes, reducing defects and improving yield. Also, the cleaning is performed without removing the chamber from the production line, minimizing downtime and ensuring the chamber remains in optimal condition for high-quality semiconductor production.
3. Cleaning Agents: Various cleaning agents are used for in situ cleaning, depending on the specific chamber materials and the types of residues to be removed. Among them, ClF3 is a highly reactive chemical often used for its residue-free cleaning capabilities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Chlorine Trifluoride as a Cleaning Gas
Chlorine Trifluoride is a valuable tool for maintaining the cleanliness and functionality of equipment. Here are some of its notable advantages:
Effectiveness: Most importantly, it can remove unwanted residues and provide residue-free cleaning. This is crucial in semiconductor manufacturing, where even tiny residues can negatively impact the quality and performance of integrated circuits.
Selectivity: It is selective in its cleaning action, targeting specific materials and contaminants without damaging or etching the underlying substrate. This property is highly beneficial in the semiconductor industry, where precision is essential.
Versatility: ClF3 efficiently removes various types of residues, including native oxides, metal fluorides, and organic contaminants, ensuring that CVD chambers remain in optimal condition for semiconductor production.
Thus, ClF3 plays a crucial role in the semiconductor industry by offering a highly effective and selective cleaning solution for CVD chambers, maintaining equipment performance, enhancing productivity, and extending equipment lifespan.
However, the use of ClF3 has some significant disadvantages:
Toxicity: It is highly toxic and poses significant safety risks to personnel, which requires strict safety protocols for handling and storage.
Reactivity: It is reactive with moisture, air, and many organic materials, potentially leading to fires or explosions if not handled with extreme care.
Specialized Handling: Due to its hazardous nature, ClF3 requires specialized handling procedures, equipment, and facilities, which can increase operational costs and complexity.
Environmental Concerns: It is a potent greenhouse gas, contributing to environmental concerns. Its use and handling must comply with strict environmental regulations, adding another layer of complexity to its management.
Safety Considerations for Handling and Storing Chlorine Trifluoride in Semiconductor Cleaning Applications
To ensure the safe use of ClF3, the semiconductor industry must follow strict safety protocols when handling and storing the gas.
It must be kept in a cool and dry place, away from any moisture or heat sources.
It must be transported and stored in specially designed containers made of materials that can withstand the highly corrosive nature of the gas.
It is crucial to use protective equipment, such as respirators, gloves, and protective clothing when working with ClF3.
Conclusion
In short, Chlorine Trifluoride is a highly effective cleaning gas with many advantages but also significant disadvantages. Besides, the semiconductor industry must take strict safety precautions when handling and storing ClF3 to prevent accidents and ensure the safe use of this critical cleaning gas. For more information, please check our homepage.
Reference:
[1] Chlorine trifluoride. (2023, August 23). In Wikipedia. https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q411305
[2] Justas Zalieckas, Paulius Pobedinskas, Martin Møller Greve, Kristoffer Eikehaug, Ken Haenen, Bodil Holst, Large area microwave plasma CVD of diamond using composite right/left-handed materials, Diamond and Related Materials, Volume 116, 2021, 108394, ISSN 0925-9635, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2021.108394.



