Therapeutic Uses of Hyaluronan
Introduction
Hyaluronic acid, also known as hyaluronan, is a naturally occurring polysaccharide found in the human body. It is a versatile molecule that plays a critical role in various biological processes, such as wound healing, tissue repair, and cell migration. In recent years, hyaluronan has gained attention as a therapeutic agent due to its impressive properties and potential therapeutic applications. In this article, we will explore the therapeutic uses of hyaluronic acid. Hope that you can have a further comprehension of the features and applications of hyaluronan.
Why Is Hyaluronan Used for Medical Practices?
Hyaluronan is utilized to make pharmaceutical supplements and assist medical surgeries for the following properties.
- Hydration: First and foremost, hyaluronic acid comes with special chemical structures. The carboxyl and hydroxyl groups inside can be connected with a large amount of water so that hyaluronic acid can attract more than 1,000 times its weight in water. It could continue to absorb water molecules from the surroundings in the long term.
- Cushion: Second, it is an important part of the fluid lying between your bones and cartilage. The fluid acts as a cushion and absorbs mechanical stress. Thus, you can walk smoothly without damaging your joints. Otherwise, there would be swelling, stiffness, joint pains, and other symptoms.
- Anti-inflammation: Last, hyaluronic acid is closely related to cell growth and differentiation. For one thing, it offers anti-inflammation effects. For another, it gives nutrients for the repair of injured cells and the growth of new cells.
With these desirable features, medical-grade hyaluronan is applied to dermatology, ophthalmology, etc.
What Are the Clinical Uses of Hyaluronan?
--Skin Products
One of the most well-known therapeutic applications of hyaluronan is in the dermatology field. It is a popular ingredient in skincare products due to its ability to hydrate and plump the skin. It is also used in dermal fillers to restore volume and smooth out wrinkles and fine lines. Hyaluronan fillers are made up of cross-linked hyaluronan molecules that provide a long-lasting effect. Stanford Chemical Company provides quality cosmetic-grade hyaluronic acid for you. Send us an inquiry if you are interested.
--Eyes
Hyaluronan has also been studied for its potential therapeutic applications in ophthalmology. For instance, hyaluronan is used as a viscoelastic agent during cataract surgery and as a treatment for dry eye syndrome. You can use artificial tears made from hyaluronic acid to relieve itchy eyes, redness, and other symptoms of dry eye syndrome. Hyaluronan can be employed in a range of ophthalmologic surgeries including corneal transplants and cataract treatment.
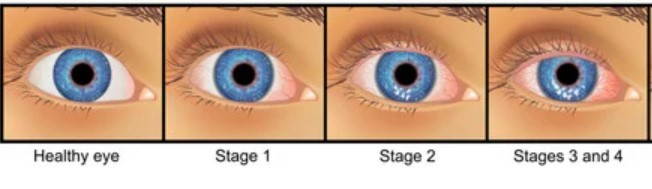
[1]
Figure 1. Four Stages of Dry Eye Disease (DED) (temporary ocular discomfort; chronic and severe pain; redness; wounds;)
--Joints
One of the unique properties of hyaluronan is its ability to bind to water molecules, which gives it a lubricating and cushioning effect. This property makes it an ideal candidate for use in joint injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage in the joints, leading to pain and stiffness. Intra-articular injections of hyaluronan can help to reduce pain, improve joint function, and delay the need for joint replacement surgery.
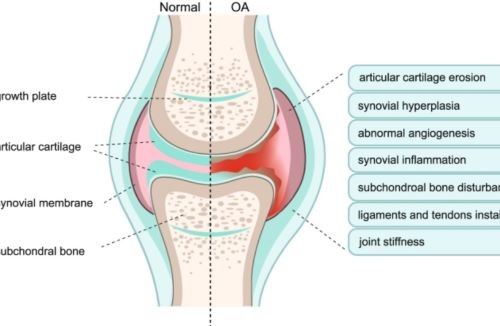
[2]
Figure 2. Osteoarthritis
--Wounds
In addition to its use in joint injections, hyaluronan has also been famous for its potential use in the treatment of chronic wounds. These wounds fail to heal within a reasonable time frame usually due to underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or poor circulation. Hyaluronan dressings have been shown to promote wound healing by providing a moist environment that supports the growth of new tissue and prevents infection.
--Burns
Hyaluronic acid works for the treatment of burns as well. Burns can cause significant tissue damage and can be difficult to treat because of the risk of infection and scarring. Hyaluronan dressings have been shown to promote wound healing and reduce scarring in patients with burn injuries.
--Cancers
Hyaluronan has been found to play a role in the development and progression of certain types of cancer, such as breast and prostate cancer. It is thought that hyaluronan promotes tumor growth and metastasis by promoting cell migration and invasion. Clinical and experimental studies have demonstrated the significance of the production and fragmentation of hyaluronic acid (HA) by tumor or peri-tumor stromal cells in the advancement of tumors [3]. Targeting hyaluronan may, therefore, be a promising approach to the treatment of cancer [3].
Related reading: Medical-grade Sodium Hyaluronate Guide 2023: Functions & Applications
Conclusion
Overall, hyaluronan is a versatile molecule with therapeutic uses in dermatology, ophthalmology, joint treatment, and wound healing thanks to its hydrating and cushioning effects. Stanford Chemicals Company has rich experience in the manufacturing and sale of medical-grade, cosmetic-grade, injection-grade, and food-grade hyaluronic acids of various molecular weights. You can check our homepage and get the perfect hyaluronan products for your projects.
Reference:
[1] Yazdani M, Elgstøen KBP, Rootwelt H, Shahdadfar A, Utheim ØA, Utheim TP. Tear Metabolomics in Dry Eye Disease: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(15):3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153755
[2] Yao, Q., Wu, X., Tao, C. et al. Osteoarthritis: pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Sig Transduct Target Ther 8, 56 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-023-01330-w
[3] Front. Immunol., 10 May 2019 Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy Volume 10 - 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00947








